Threat Trends: Email Landscape
As organizations and security teams around the world continue to improve their cyber hygiene and strengthen the defenses of their digital environments, threat actors are being forced to adapt and employ more advanced, sophisticated attack methods to achieve their goals.
Vendor Email Compromise (VEC) is one such elaborate and sophisticated type of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack which exploits pre-existing trusted business relationships to impersonate vendors, with the goal of launching a targeted attack on the vendor’s customers [1].
In March 2023, Darktrace/Email™ detected an example of a VEC attack on the network of a customer in the energy sector. Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI worked to successfully neutralize the VEC attack before it was able to take hold, by blocking the malicious emails so that they did not reach the inboxes of the intended recipients.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC is the practice of using deceitful emails to trick an organization into transferring funds or divulging sensitive information to a malicious actor. BEC attacks can have devastating financial consequences for organizations, with the FBI reporting a total of USD 2.7 billion in losses from BEC attacks in 2022 [2]. Along with ransomware attacks, BEC attacks are one of the greatest cyber threats facing organizations.
Vendor Email Compromise (VEC)
VEC represents a “new milestone in the evolution of BEC attacks” having taken BEC attacks “to a whole new level of sophistication” [3]. Traditional BEC attacks involve the impersonation of an upper or middle-management employee by a cybercriminal, who attempts to trick a senior executive or employee with access to the company’s finances into transferring funds [4]. Thus, they are crafted to target a specific individual within an organization.
On the other hand, VEC attack campaigns take this attack style even further as they tend to require a greater understanding of existing vendor-customer business relationships. A cyber-criminal gains access to a legitimate vendor account, the process of which may take months to design and fully implement, and uses the account to spread malicious emails to the vendor’s customers. VEC attacks are complex and difficult to detect, however they share some common features [1,3]:
1. Reconnaissance on the vendor and their customer base – the threat actor conducts in-depth research in an attempt to be as convincing as possible in their impersonation efforts. This process may take weeks or months to complete.
2. Credential stealing through phishing campaigns – the threat actor tricks the vendor’s employees into revealing confidential data or corporate credentials in order to gain access to one of the email accounts belonging to the vendor.
3. Account takeover - once the attacker has gained access to one of the vendor’s email accounts, they will create mailbox rules which forward emails meeting certain conditions (such as having ‘Invoice’ in their subject line) to the threat actor’s inbox. This is typically a lengthy process and requires the malicious actors to harvest as much sensitive information as they need in order to successfully masquerade as vendor employees.
4. Deceitful emails are sent to the vendor’s customers – the attacker crafts and sends a highly sophisticated and difficult to detect email campaign to targeted individuals amongst the vendor’s customers. These emails, which may be embedded into existing email threads, will typically contain instructions on how to wire money to the bank account of an attacker.
There have been many high-profile cases of BEC attacks over the years, one of the most famous being the vendor-impersonating BEC attacks carried out between 2013 and 2015 [5]. This BEC campaign resulted in victim companies transferring a total of USD 120 million to bank accounts under the attacker’s control. As the threat of BEC, and in particular VEC, attacks continue to rise, so too does the importance of being able to detect and respond to them.
Observed VEC Attack
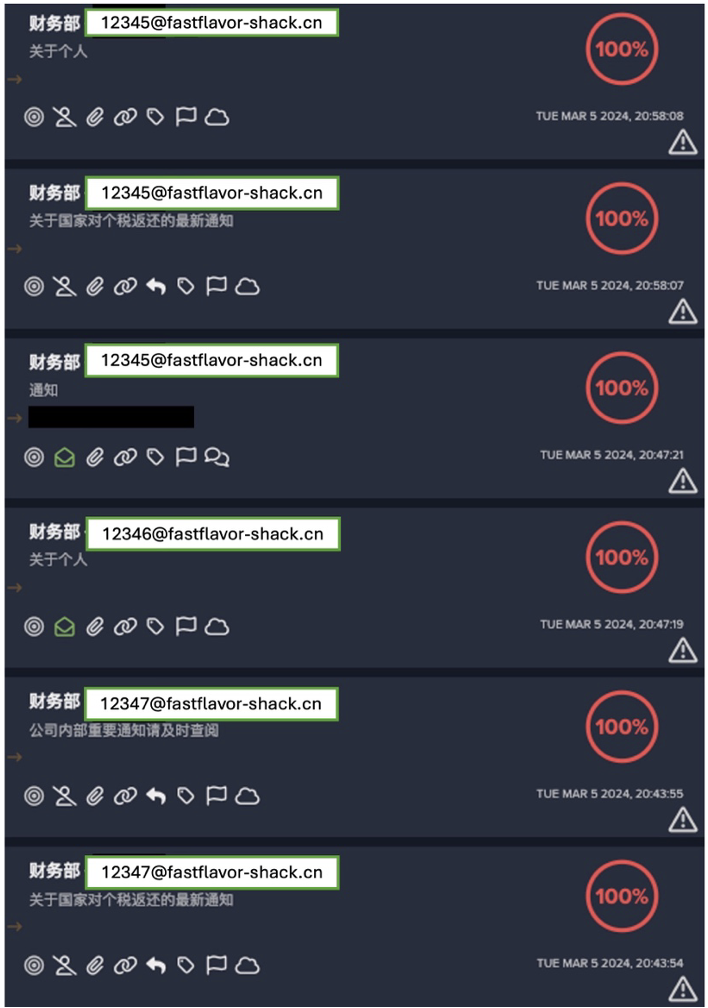
In March 2023, Darktrace/Email observed a VEC attack on an energy company. Email communication between this customer and one of their third-party vendors was common and took place as part of expected business activity, earning previous emails tags such as “Known Domain Relationship”, “Known Correspondent”, and “Established Domain Relationship”. These tags identify the sender relationship as trusted, causing Darktrace’s AI to typically attribute an anomaly score of 0% to emails from this third-party sender.
Just fifty minutes after the above legitimate email was observed, a group of suspicious emails were sent from the same domain, indicating that the trusted third-party had been compromised. Darktrace’s AI picked up on the peculiarity of these emails straight away, detecting elements of the mails which were out of character compared to the sender’s usual pattern of life, and as a result attributing these emails a 100% anomaly score despite the trusted relationship between the customer and sender domain. These suspicious emails were part of a targeted phishing attack, sent to high value individuals such as the company’s CTO and various company directors.

Using methods outside of Darktrace’s visibility, a malicious actor managed to hijack the corporate account of a senior employee of this vendor company. The actor abused this email account to send deceitful emails to multiple employees at the energy company, including senior executives.
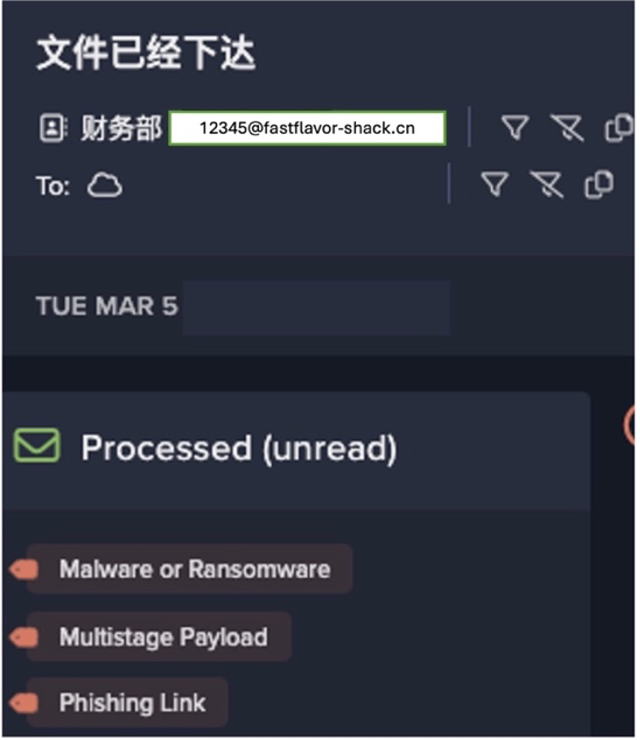
Each of the emails sent by the attacker contained a link to a malicious file hosted inside a SharePoint repository associated with a university that had no association with the energy company. The malicious actor therefore appears to have leveraged a previously hijacked SharePoint repository to host their payload.
Cyber-criminals frequently use legitimate file storage domains to host malicious payloads as traditional gateways often fail to defend against them using reputation checks. The SharePoint file which the attacker sought to distribute to employees of the energy company likely provided wire transfer or bank account update instructions. If the attacker had succeeded in delivering these emails to these employees’ mailboxes, then the employees may have been tricked into performing actions resulting in the transfer of funds to a malicious actor. However, the attacker’s attempts to deliver these emails were thwarted by Darktrace/Email.
Darktrace Coverage
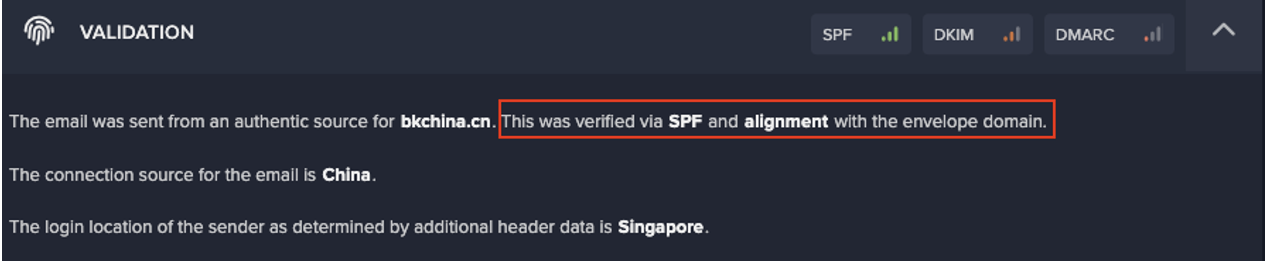
Despite the malicious actor sending their deceitful emails from a trusted vendor account, a range of anomalies were detected by Darktrace’s AI, causing the malicious emails to be given a 100% anomaly score and thus held from their recipients’ mailboxes. Such abnormalities, which represented a deviation in normal behavior, included:
- The presence of an unexpected, out of character file storage link (known to be used for hosting malicious content)
- The geographical source of the email
- The anomalous linguistic structure and content of the email body, which earned the emails a high inducement score

Darktrace has a series of models designed to trigger when anomalous features, such as those described above, are detected. The emails which made up this particular VEC attack breached a number of notable Darktrace/Email models. The presence of the suspicious link in the emails caused multiple link-related models to breach, which in turn elicited Darktrace RESPOND™ to perform its ‘double lock link’ action – an action which ensures that a user who has clicked on it cannot follow it to its original source. Models which breached due to the suspicious SharePoint link include:
Link / Link To File Storage
- Link / Low Link Association
- Link / New Unknown Link
- Link / Outlook Hijack
- Link / Relative Sender Anomaly + New Unknown Link
- Link / Unknown Storage Service
- Link / Visually Prominent Link Unexpected for Sender
- Unusual / Unusual Login Location + Unknown Link
The out-of-character and suspicious linguistic aspects of the emails caused the following Darktrace/Email models to breach:
- High Anomaly Sender
- Proximity / Phishing
- Proximity / Phishing and New Activity
- Unusual / Inducement Shift High
- Unusual / Undisclosed Recipients
- Unusual / Unusual Login Location
- Unusual / Off Topic
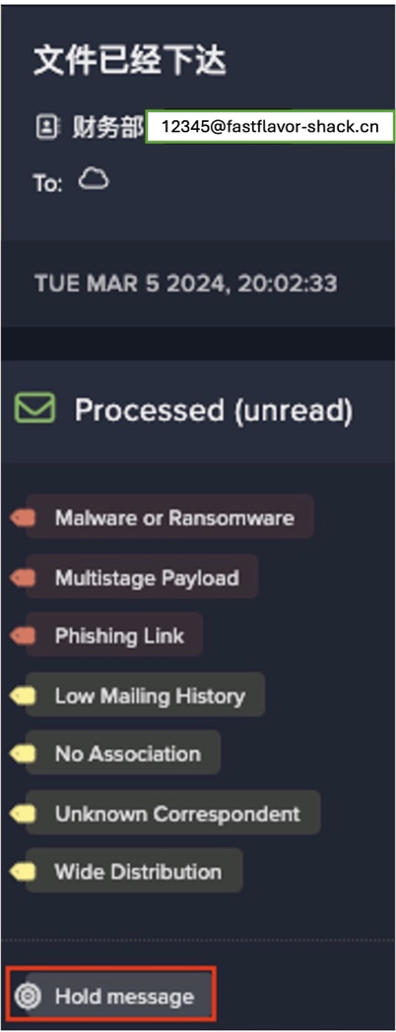
Due to the combination of suspicious features that were detected, tags such as ‘Phishing Link’ and ‘Out of Character’ were also added to these emails by Darktrace/Email. Darktrace’s coverage of these emails’ anomalous features ultimately led Darktrace RESPOND to perform its most severe inhibitive action, ‘hold message’. Applying this action stopped the emails from entering their recipients’ mailboxes. By detecting deviations from the sender’s normal email behavior, Darktrace/Email was able to completely neutralize the emails, and prevent them from potentially leading to significant financial harm.
Conclusion
Despite bypassing the customer’s other security measures, Darktrace/Email successfully identified and held these malicious emails, blocking them from reaching the inboxes of the intended recipients and thus preventing a successful targeted VEC attack. The elaborate and sophisticated nature of VEC attacks makes them particularly perilous to customers, and they can be hard to detect due to their exploitation of trusted relationships, and in this case, their use of legitimate services to host malicious files.
Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection means it is uniquely placed to identify deviations in common email behavior, while its autonomous response capabilities allow it to take preventative action against emerging threats without latency.
Credits to: Sam Lister, Senior Analyst, for his contributions to this blog.
Appendices
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Tactic - Techniques
Resource Development
- T1586.002 – Compromise Accounts: Email Accounts
- T1584.006 – Compromise Infrastructure: Web Services
- T1608.005 – Stage Capabilities: Link Target
Initial Access
- T1195 – Supply Chain Compromise
- T1566.002 – Phishing : Spearphishing Link
References
[1] https://www.cloudflare.com/en-gb/learning/email-security/what-is-vendor-email-compromise/
[2] https://www.ic3.gov/Media/PDF/AnnualReport/2022_IC3Report.pdf
[3] https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/vendor-email-compromise-vec/
[4] https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/files/Business-email-compromise-infographic.pdf
[5] https://www.justice.gov/usao-sdny/pr/lithuanian-man-sentenced-5-years-prison-theft-over-120-million-fraudulent-business