What is Business Email Compromise (BEC)?
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is the practice of tricking an organization into transferring funds or sensitive data to a malicious actor.
Although at face value this type of attack may not carry the same gravitas as the more blockbuster, cloak-and-dagger type of attack such as ransomware [1], the costs of BEC actually dwarf that of ransomware [2]. Moreover, among UK organizations that reported a cyber breach in 2023, attacks related to BEC – namely phishing attacks, email impersonation, attempted hacking of online back accounts, and account takeover – were reported as the most disruptive, ahead of ransomware and other types of cyber-attack [3].
What makes a BEC attack successful?
BEC attacks are so successful and damaging due to the difficulty of detection for traditional security systems, along with their ease of execution. BEC does not require much technical sophistication to accomplish; rather, it exploits humans’ natural trust in known correspondents, via a phishing email for example, to induce them to perform a certain action.
How does a BEC attack work?
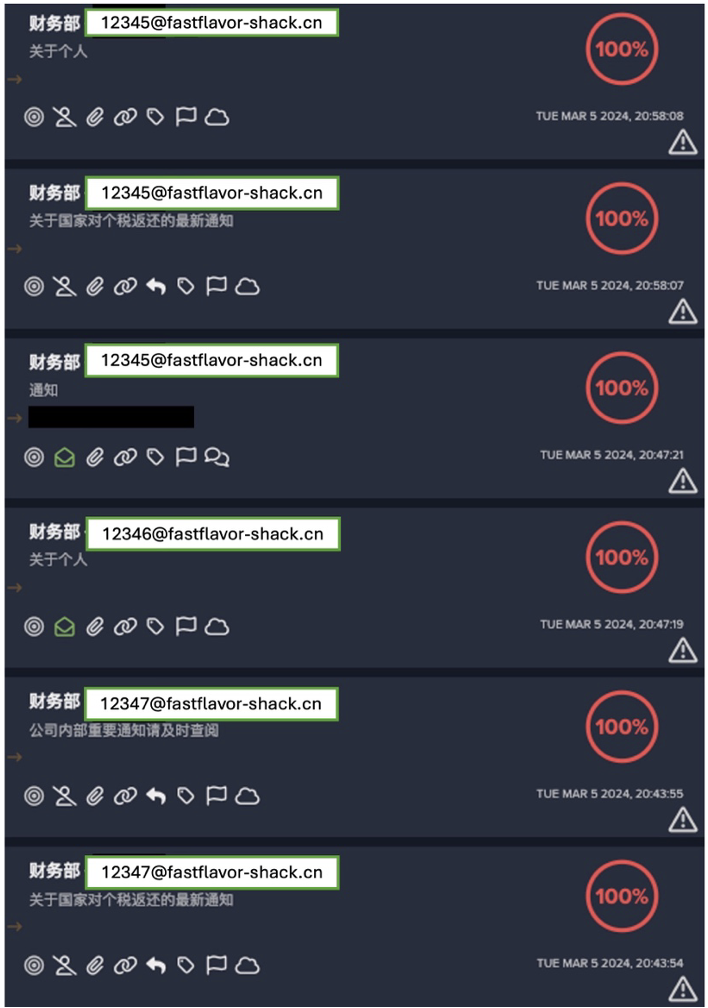
BEC attacks typically begin with a phishing email to an employee of an organization. Traditional email gateways may be unable to block the initial phishing email, as the email often appear to have been sent by a known correspondent, or it may contain minimal payload content.
The recipient’s interaction with the initial phishing email will likely result in the attacker gaining access to the user’s identity. Once access is obtained, the attacker may abuse the identity of the compromised user to obtain details of the user’s financial relations to the rest of the organization or its customers, eventually using these details to conduct further malicious email activity, such as sending out emails containing fraudulent wire transfer requests. Today, the continued growth in adoption of services to support remote working, such as cloud file storage and sharing, means that the compromise of a single user’s email account can also grant access to a wide range of corporate sensitive information.
How to protect against BEC attacks
The rapid uptake of cloud-based infrastructure and software-as-a-service (SaaS) outpaces the adoption of skills and expertise required to secure it, meaning that security teams are often less prepared to detect and respond to cloud-based attacks.
Alongside the adoption of security measures that specialize in anomaly-based detection and autonomous response, like Darktrace DETECT™ and Darktrace RESPOND™, it is extremely beneficial for organizations to have an around the clock security operations center (SOC) in place to monitor and investigate ongoing suspicious activity as it emerges.
In June 2023, Darktrace’s SOC alerted a customer to an active BEC attack within their cloud environment, following the successful detection of suspicious activity by Darktrace’s AI, playing a fundamental role in thwarting the attack in its early stages.
Darktrace Mitigates BEC Attack

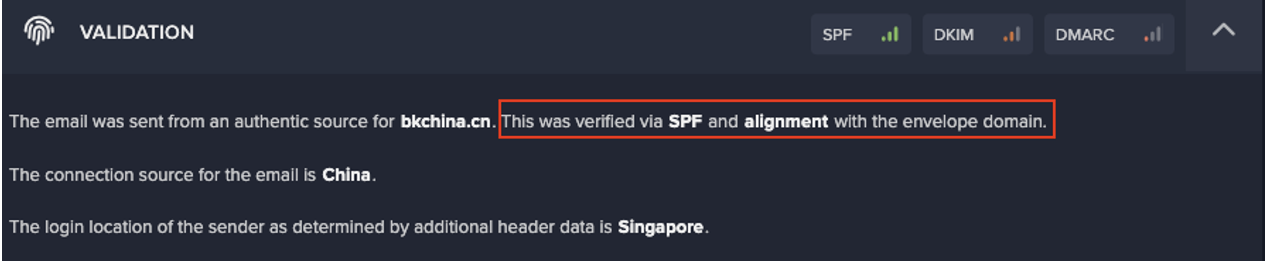
It was suspected the attack began with a phishing email, as on the previous day the user had received a highly anomalous email from an external sender with which the organization had not previously communicated. However, the customer had configured Darktrace/Email™ in passive mode, which meant that Darktrace was not able to carry out any RESPOND actions on this anomalous email to prevent it from landing in the user’s inbox. Despite this, Darktrace/Apps was able to instantly detect the subsequent unusual login to the customer’s SaaS environment; its anomaly-based approach to threat detection allowed it to recognize the anomalous behavior even though the malicious email had successfully reached the user.
Following the anomalous ExpressVPN login, Darktrace detected further account anomalies originating from another ExpressVPN IP (45.92.229[.]195), as the attacker accessed files over SharePoint. Notably, Darktrace identified that the logins from ExpressVPN IPs were performed with the software Chrome 114, however, activity from the legitimate account owner prior to these unusual logins was performed using the software Chrome 102. It is unusual for a user to be using multiple browser versions simultaneously, therefore in addition to the observed impossible travel, this further implied the presence of different actors behind the simultaneous account activity.

Darktrace identified that the files observed during this anomalous activity referenced financial information and personnel schedules, suggesting that the attacker was performing internal reconnaissance to gather information about sensitive internal company procedures, in preparation for further fraudulent financial activity.
Although the actions taken by the attacker were mostly passive, Darktrace/Apps chained together the multiple anomalies to understand that this pattern of activity was indicative of movement along the cyber kill chain. The multiple model breaches generated by the ongoing unusual activity triggered an Enhanced Monitoring model breach that was escalated to Darktrace’s SOC as the customer had subscribed to Darktrace’s Proactive Threat Notification (PTN) service. Enhanced Monitoring models detect activities that are more likely to be indicative of compromise.
Subsequently, Darktrace’s SOC triaged the activity detected on the SaaS account and sent a PTN alert to the customer, advising urgent follow up action. The encrypted alert contained relevant technical details of the incident that were summarized by an expert Darktrace Analyst, along with recommendations to the customer’s internal SOC team to take immediate action. Upon receipt and validation of the alert, the customer used Darktrace RESPOND to perform a manual force logout and block access from the external ExpressVPN IP.
Had Darktrace RESPOND been enabled in autonomous response mode, it would have immediately taken action to disable the account after ongoing anomalies were detected from it. However, as the customer only had RESPOND configured in the manual human confirmation model, the expertise of Darktrace’s SOC team was critical in enabling the customer to react and prevent further escalation of post-compromise activity. Evidence of further attempts to access the compromised account were observed hours after RESPOND actions were taken, including failed login attempts from another rare external IP, this time associated with the VPN service NordVPN.

Because the customer had subscribed to Darktrace’s PTN service, they were able to further leverage the expertise of Darktrace’s global team of cyber analysts and request further analysis of which files were accessed by the legitimate account owner versus the attacker. This information was shared securely within the same Customer Portal ticket that was automatically opened on behalf of the customer when the PTN was alerted, allowing the customer’s security team to submit further queries and feedback, and request assistance to further investigate this alert within Darktrace. A similar service called Ask the Expert (ATE) exists for customers to draw from the expertise of Darktrace’s analysts at any time, not just when PTNs are alerted.
Conclusion
The growing prevalence and impact of BEC attacks amid the shift to cloud-based infrastructure means that already stretched internal security teams may not have the sufficient human capacity to detect and respond to these threats.
Darktrace’s round-the-clock SOC thwarted a BEC attack that had the potential to result in significant financial and reputational damage to the legal services company, by alerting the customer to high priority activity during the early stages of the attack and sharing actionable insights that the customer could use to prevent further escalation. Following the confirmed compromise, the support and in-depth analysis provided by Darktrace’s SOC on the files accessed by the attacker enabled the customer to effectively report this breach to the Information Commissioner’s Office, to maintain compliance with UK data protection regulations. [4].
Although the attacker used IP addresses that were local to the customer’s country of operations and did not perform overtly noisy actions during reconnaissance, Darktrace was able to identify that this activity deviated from the legitimate user’s typical pattern of life, triggering model breaches at each stage of the attack as it progressed from initial access to internal reconnaissance. While Darktrace RESPOND triggered an action that would have prevented the attack autonomously, the customer’s configuration meant that Darktrace’s SOC had an even more significant role in alerting the customer directly to take manual action.
Credit to: Sam Lister, Senior Analyst, for his contributions to this blog.
Appendices
Darktrace DETECT/Apps Models Breached:
- SaaS / Access / Unusual External Source for SaaS Credential Use
- SaaS / Compromise / Login From Rare Endpoint While User Is Active
- SaaS / Unusual Activity / Activity from Multiple Unusual IPs
- SaaS / Unusual Activity / Multiple Unusual SaaS Activities
- SaaS / Access / Suspicious Login Attempt
- SaaS / Compromise / SaaS Anomaly Following Anomalous Login (Enhanced Monitoring Model)
Darktrace RESPOND/Apps Models Breached:
- Antigena / SaaS / Antigena Unusual Activity Block
- Antigena / SaaS / Antigena Suspicious SaaS Activity Block
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
References
[1] Rand, D. (2022, November 10). Why Business Email Compromise Costs Companies More Than Ransomware Attacks. Retrieved from Tanium: https://www.tanium.com/blog/whybusiness-email-compromise-costs-companies-more-than-ransomware-attacks/
[2] Federal Bureau of Investigation. (2022). 2022 IC3 Report. Retrieved from IC3.gov: https://www.ic3.gov/Media/PDF/AnnualReport/2022_IC3Report.pdf
[3] Department for Science, Innovation & Technology. (2023, April 19). Cyber security breaches survey 2023. Retrieved from gov.uk: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/cyber-security-breaches-survey-2023/cybersecurity-breaches-survey-2023
[4] ICO. (2023). Personal data breaches: a guide. Retrieved from Information Commissioner's Office: https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/report-a-breach/personal-data-breach/personal-data-breaches-a-guide/#whatbreachesdo