Introduction
As the threat of costly cyber-attacks continues represent a real concern to security teams across the threat landscape, more and more organizations are strengthening their defenses with additional security tools to identify attacks and protect their networks. As a result, malicious actors are being forced to adapt their tactics, modify existing variants of malicious software, or utilize entirely new variants.
Symantec recently released an article about Syssphinx, the financially motivated cyber threat group previously known for their point-of-sale attacks. Syssphinx attempts to deploy ransomware on customer networks via a modified version of their ‘Sardonic’ backdoor. Such activity highlights the ability of threat actors to alter the composition and presentation of payloads, tools, and tactics.
Darktrace recently detected some of the same indicators suggesting a likely Syssphinx compromise within the network of a customer trialing the Darktrace DETECT™ and RESPOND™ products. Despite the potential for variations in the construction of backdoors and payloads used by the group, Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection allowed it to stitch together a detailed account of compromise activity and identify the malicious activity prior to disruptive events on the customer’s network.
What is Syssphinx?
Syssphinx is a notorious cyber threat entity known for its financially motivated compromises. Also referred to as FIN8, Syssphinx has been observed as early as 2016 and is largely known to target private sector entities in the retail, hospitality, insurance, IT, and financial sectors.[1]
Although Syssphinx primarily began focusing on point-of-sale style attacks, the activity associated with the group has more recently incorporated ransomware variants into their intrusions in a potential bid to further extract funds from target organizations.[2]
Syssphinx Sardonic Backdoor
Given this gradual opportunistic incorporation of ransomware, it should not be surprising that Syssphinx has slowly expanded its repertoire of tools. When primarily performing point-of-sale compromises, the group was known for its use of point-of-sale specific malwares including BadHatch, PoSlurp/PunchTrack, and PowerSniff/PunchBuggy/ShellTea.[3]
However, in a seeming response to updates in detection systems while using previous indicators of compromise (IoCs), Syssphinx began to modify its BadHatch malware. This resulted in the use of a C++ derived backdoor known as “Sardonic”, which has the ability to aggregate host credentials, spawn additional command sessions, and deliver payloads to compromised devices via dynamic-link library (DLL).[4],[5]
Analysis of the latest version of Sardonic reveals further changes to the malware to elude detection. These shifts include the implementation of the backdoor in the C programming language, and additional over-the-network communication obfuscation techniques. [6]
During the post-exploitation phase, the group tends to rely on “living-off-the-land” tactics, whereby an attacker utilizes tools already present within the organization’s digital environment to avoid detection. Syssphinx seems to utilize system-native tools such as PowerShell and the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) interface.[7] It is also not uncommon to see Windows-based vulnerability exploits employed on compromised devices. This has been observed by researchers who have examined previous iterations of Syssphinx backdoors.[8] Syssphinx also appears to exhibit elements of strategic patience and discipline in its operations, with significant time gaps in operations noted by researchers. During this time, it appears likely that updates and tweaks were applied to Syssphinx payloads.
Compromise Details
In late April 2023, Darktrace identified an active compromise on the network of a prospective customer who was trialing Darktrace DETECT+RESPOND. The customer, a retailer in EMEA with hundreds of tracked devices, reached out to the Darktrace Analyst team via the Ask the Expert (ATE) service for support and further investigation, following the encryption of their server and backup data storage in an apparent ransomware attack. Although the encryption events fell outside Darktrace’s purview due to a limited set up of trial appliances, Darktrace was able to directly track early stages of the compromise before exfiltration and encryption events began. If a full deployment had been set up and RESPOND functionality had been configured in autonomous response mode, Darktrace may have helped mitigate such encryption events and would have aided in the early identification of this ransomware attack.
Initial Intrusion and Establishment of Command and Control (C2) Infrastructure
As noted by security researchers, Syssphinx largely relies on social engineering and phishing emails to deliver its backdoor payloads. As there were no Darktrace/Email™ products deployed for this customer, it would be difficult to directly observe the exact time and manner of initial payload delivery related to this compromise. This is compounded by the fact that the customer had only recently began using Darktrace’s products during their trial period. Given the penchant for patience and delay by Syssphinx, it is possible that the intrusion began well before Darktrace had visibility of the organization’s network.
However, beginning on April 30, 2023, at 07:17:31 UTC, Darktrace observed the domain controller dc01.corp.XXXX making repeated SSL connections to the endpoint 173-44-141-47[.]nip[.]io. In addition to the multiple open-source intelligence (OSINT) flags for this endpoint, the construction of the domain parallels that of the initial domain used to deliver a backdoor, as noted by Symantec in their analysis (37-10-71-215[.]nip[.]io). This activity likely represented the initial beaconing being performed by the compromised device. Additionally, an elevated level of incoming external data over port 443 was observed during this time, which may be associated with the delivery of the Sardonic backdoor payload. Given the unusual use of port 443 to perform SSH connections later seen in the kill chain of this attack, this activity could also parallel the employment of embedded backdoor payloads seen in the latest iteration of the Sardonic backdoor noted by Symantec.

Regardless, the domain controller proceeded to make repeated connections over port 443 to the noted domain.

Internal Reconnaissance/Privilege Escalation
Following the establishment of C2 communication, Darktrace detected numerous elements of internal reconnaissance. On Apr 30, 2023, at 22:06:26 UTC, the desktop device desktop_02.corp.XXXX proceeded to perform more than 100 DRSGetNCChanges requests to the aforementioned domain controller. These commands, which are typically implemented over the RPC protocol on the DRSUAPI interface, are frequently utilized in Active Directory sync attacks to copy Active Directory information from domain controllers. Such activity, when not performed by new domain controllers to sync Active Directory contents, can indicate malicious domain or user enumeration, credential compromise or Active Directory enumeration.
Although the affected device made these requests to the previously noted domain controller, which was already compromised, such activity may have further enabled the compromise by allowing the threat actor to transfer these details to a more easily manageable device.
The device performing these DRSGetNCChanges requests would later be seen performing lateral movement activity and making connections to malicious endpoints.

Execution and Lateral Movement
At 23:09:53 UTC on April 30, 2023, the original domain server proceeded to make multiple uncommon WMI calls to a destination server on the same subnet (server01.corp.XXXX). Specifically, the device was observed making multiple RPC calls to IWbem endpoints on the server, which included login and ExecMethod (method execution) commands on the destination device. This destination device later proceeded to conduct additional beaconing activity to C2 endpoints and exfiltrate data.

Similarly, beginning on May 1, 2023, at 00:11:09 UTC, the device desktop_02.corp.XXXX made multiple WMI requests to two additional devices, one server and one desktop, within the same subnet as the original domain controller. During this time, desktop_02.corp.XXXX also utilized SMBv1, an outdated and typically non-compliant version communication protocol, to write the file rclone.exe to the same two destination devices. Rclone.exe, and its accompanying bat file, is a command-line tool developed by IT provider Rclone, to perform file management tasks. During this time, Darktrace also observed the device reading and deleting an unexpected numeric file on the ADMIN$ of the destination server, which may represent additional defense evasion techniques and tool staging.


Given that the net loader sample analyzed by Symantec injects the backdoor into a WmiPrvSE.exe process, the use of WMI operations is not unexpected. Employment of WMI also correlates with the previously mentioned “living-off-the-land” tactics, as WMI services are commonly used for regular network and system administration purposes. Moreover, the staging of rclone.exe, a legitimate file management tool, for data exfiltration underscores attempts to blend into existing and expected network traffic and remain undetected on the customer’s network.
Data Exfiltration and Impact
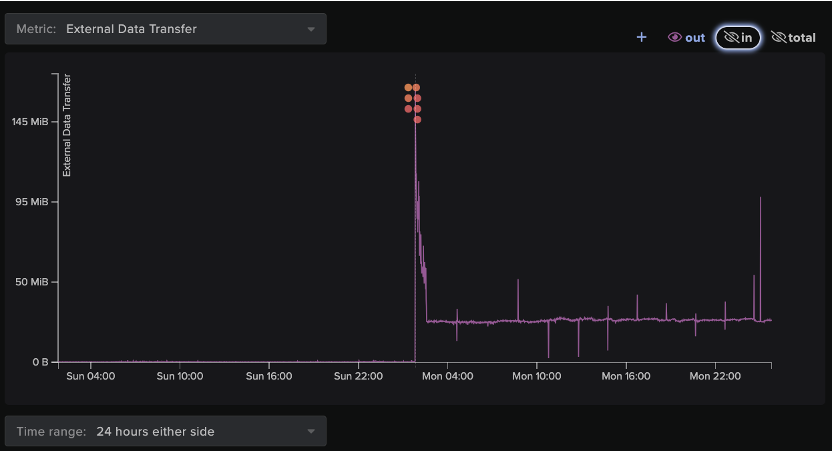
Initial stages of data exfiltration actually began prior to some of the lateral movement events described above. On April 30, 2023, 23:09:47 the device server01.corp.XXXX, transferred nearly 11 GB of data to 173.44[.]141[.]47, as well as to the rare external IP address 170.130[.]55[.]77, which appears to have served as the main exfiltration destination during this compromise. Furthermore, the host made repeated connections to the same external IP associated with the initial suspicious beaconing activity (173.44[.]141[.]47) over SSL.
While the data exfiltration event unfolded, the device, server01.corp.XXXX, made multiple HTTP requests to 37.10[.]71[.]215, which featured URIs requesting the rclone.exe and rclone.bat files. This IP address was directly involved in the sample analyzed by Symantec. Furthermore, one of the devices that received the SMB file writes of rclone.exe and the WMI commands from desktop_02.corp.XXXX also performed SSL beaconing to endpoints associated with the compromise.
Between 01:20:45 - 03:31:41 UTC on May 1, 2023, a Darktrace detected a series of devices on the network performing a repeated pattern of activity, namely external connectivity followed by suspicious file downloads and external data transfer operations. Specifically, each affected device made multiple HTTP requests to 37.10[.]71[.]215 for rclone files. The devices proceeded to download the executable and/or binary files, and then transfer large amounts of data to the aforementioned endpoints, 170.130[.]55[.]77 and or 173-44-141-47[.]nip[.]io. Although the devices involved in data exfiltration utilized port 443 as a destination port, the connections actually used the SSH protocol. Darktrace recognized this behavior as unusual as port 443 is typically associated with the SSL protocol, while port 22 is reserved for SSH. Therefore, this activity may represent the threat actor’s attempts to remain undetected by security tools.
This unexpected use of SSH over port 443 also correlates with the descriptions of the new Sardonic backdoor according to threat researchers. Further beaconing and exfiltration activity was performed by an additional host one day later whereby the device made suspicious repeated connections to the aforementioned external hosts.

In total, nine separate devices were involved in this pattern of activity. Five of these devices were labeled as ‘administrative’ devices according to their hostnames. Over the course of the entire exfiltration event, the attackers exfiltrated almost 61 GB of data from the organization’s environment.
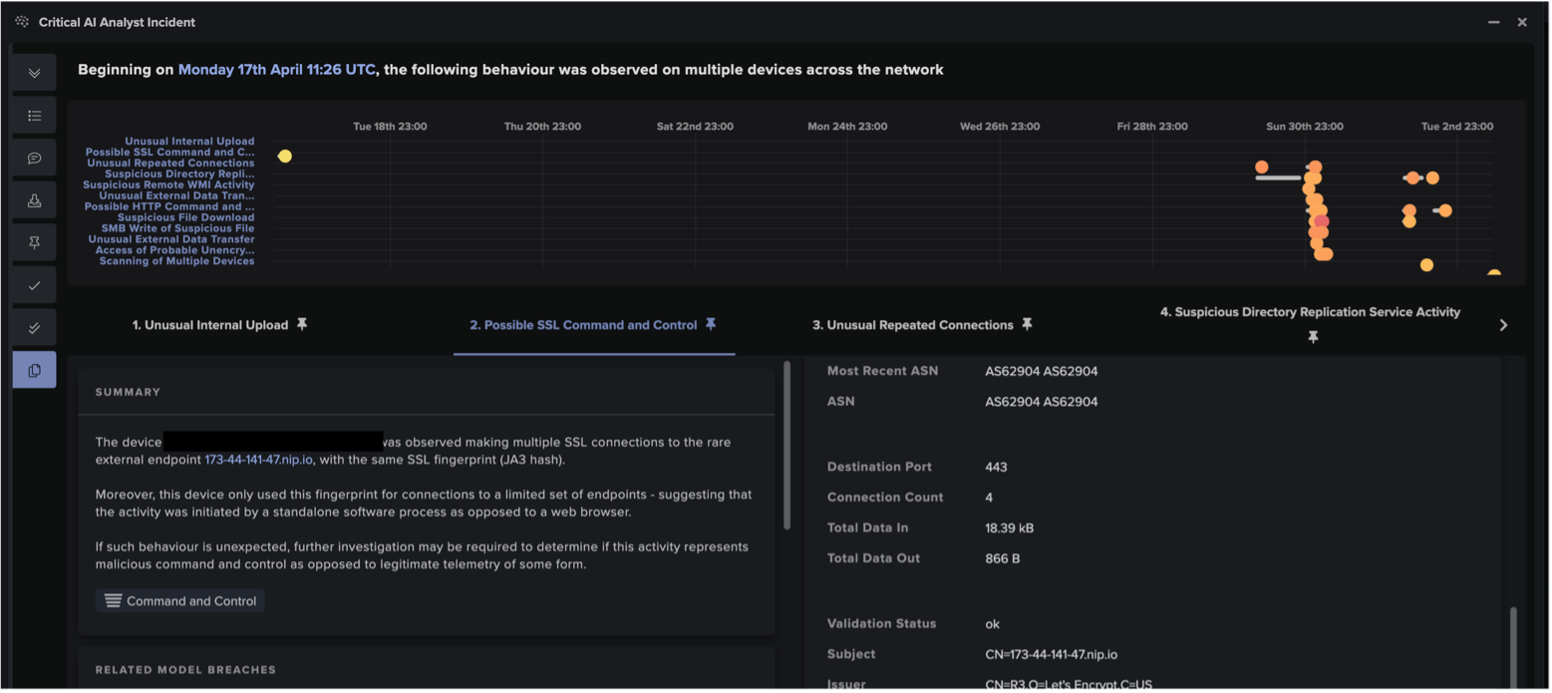
In addition to the individual anomaly detections by DETECT, Darktrace’s Cyber AI Analyst™ launched an autonomous investigation into the unusual behavior carried out by affected devices, connecting and collating multiple security events into one AI Analyst Incident. AI Analyst ensures that Darktrace can recognize and link the individual steps of a wider attack, rather than just identifying isolated incidents. While traditional security tools may mistake individual breaches as standalone activity, Darktrace’s AI allows it to provide unparalleled visibility over emerging attacks and their kill chains. Furthermore, Cyber AI Analyst’s instant autonomous investigations help to save customer security teams invaluable time in triaging incidents in comparison with human teams who would have to commit precious time and resources to conduct similar pattern analysis.
In this specific case, AI Analyst identified 44 separate security events from 18 different devices and was able to tie them together into one incident. The events that made up this AI Analyst Incident included:
- Possible SSL Command and Control
- Possible HTTP Command and Control
- Unusual Repeated Connections
- Suspicious Directory Replication ServiceActivity
- Device / New or Uncommon WMI Activity
- SMB Write of Suspicious File
- Suspicious File Download
- Unusual External Data Transfer
- Unusual External Data Transfer to MultipleRelated Endpoints
Had Darktrace RESPOND been enabled in autonomous response mode on the network of this prospective customer, it would have been able to take rapid mitigative action to block the malicious external connections used for C2 communication and subsequent data exfiltration, ideally halting the attack at this stage. As previously discussed, the limited network configuration of this trial customer meant that the encryption events unfortunately took place outside of Darktrace’s scope. When fully configured on a customer environment, Darktrace DETECT can identify such encryption attempts as soon as they occur. Darktrace RESPOND, in turn, would be able to immediately intervene by applying preventative actions like blocking internal connections that may represent file encryption, or limiting potentially compromised devices to a previously established pattern of life, ensuring they cannot carry out any suspicious activity.
Conclusion
Despite the limitations posed by the customer’s trial configuration, Darktrace demonstrated its ability to detect malicious activity associated with Syssphinx and track it across multiple stages of the kill chain.
Darktrace’s ability to identify the early stages of a compromise and various steps of the kill chain, highlights the necessity for machine learning-enabled, anomaly-based detection. In the face of threats such as Syssphinx, that exhibit the propensity to recast backdoor payloads and incorporate on “living-off-the-land” tactics, signatures and rules-based detection may not prove as effective. While Syssphinx and other threat groups will continue to adopt new tools, methods, and techniques, Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI is uniquely positioned to meet the challenge of such threats.
Appendix
DETECT Model Breaches Observed
• Anomalous Server Activity / Anomalous External Activity from Critical Network Device
• Anomalous Connection / Anomalous DRSGetNCChanges Operation
• Device / New or Uncommon WMI Activity
• Compliance / SMB Drive Write
• Anomalous Connection / Data Sent to Rare Domain
• Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1 GiB Outbound
• Unusual Activity / Unusual External Data Transfer
• Unusual Activity / Unusual External Data to New Endpoints
• Compliance / SSH to Rare External Destination
• Anomalous Connection / Unusual SMB Version 1 Connectivity
• Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External Location
• Anomalous File / Script from Rare External Location
• Compromise / Suspicious File and C2
• Device / Initial Breach Chain Compromise
AI Analyst Incidents Observed
• Possible SSL Command and Control
• Possible HTTP Command and Control
• Unusual Repeated Connections
• Suspicious Directory Replication Service Activity
• Device / New or Uncommon WMI Activity
• SMB Write of Suspicious File
• Suspicious File Download
• Unusual External Data Transfer
• Unusual External Data Transfer to Multiple Related Endpoints
IoCs
IoC - Type - Description
37.10[.]71[.]215 – IP – C2 + payload endpoint
173-44-141-47[.]nip[.]io – Hostname – C2 – payload
173.44[.]141[.]47 – IP – C2 + potential payload
170.130[.]55[.]77 – IP – Data exfiltration endpoint
Rclone.exe – Exe File – Common data tool
Rclone.bat – Script file – Common data tool
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Command and Control
T1071 - Application Layer Protocol
T1071.001 – Web protocols
T1573 – Encrypted channels
T1573.001 – Symmetric encryption
T1573.002 – Asymmetric encryption
T1571 – Non-standard port
T1105 – Ingress tool transfer
Execution
T1047 – Windows Management Instrumentation
Credential Access
T1003 – OS Credential Dumping
T1003.006 – DCSync
Lateral Movement
T1570 – Lateral Tool Transfer
T1021 - Remote Services
T1021.002 - SMB/Windows Admin Shares
T1021.006 – Windows Remote Management
Exfiltration
T1048 - Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol
T1048.001 - Exfiltration Over Symmetric Encrypted Non-C2 Protocol
T1048.002 - Exfiltration Over Symmetric Encrypted Non-C2 Protocol
T1041 - Exfiltration Over C2 Channel
References
[1] https://cyberscoop.com/syssphinx-cybercrime-ransomware/
[2] https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/Syssphinx-FIN8-backdoor
[3] https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/fin8-deploys-alphv-ransomware-using-sardonic-malware-variant/
[4] https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/Syssphinx-FIN8-backdoor
[5] https://thehackernews.com/2023/07/fin8-group-using-modified-sardonic.html
[6] https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/Syssphinx-FIN8-backdoor
[7] https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/Syssphinx-FIN8-backdoor
[8] https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/windows-zero-day-payment-cards





























.jpg)

.webp)










