The modern security team faces challenges on all fronts – it is too often overstretched dealing with an increased attack surface, enabling workforces for secure remote work, and managing multiple security tools to protect that workforce. Added to that, the surge in more sophisticated phishing campaigns – now supported by AI tools – means that it’s harder than ever to pre-empt attacks.
The needs of the security team should be a key consideration when deploying an email security solution, as it’s them who will be accountable for the success and maintenance of the product. Minimizing time spent inside the user interface – through trusted detection and response technology combined with intuitive reporting and optimized workflows – should be front of mind for vendors in order to assure teams of their value.
Taking security teams off the frontline
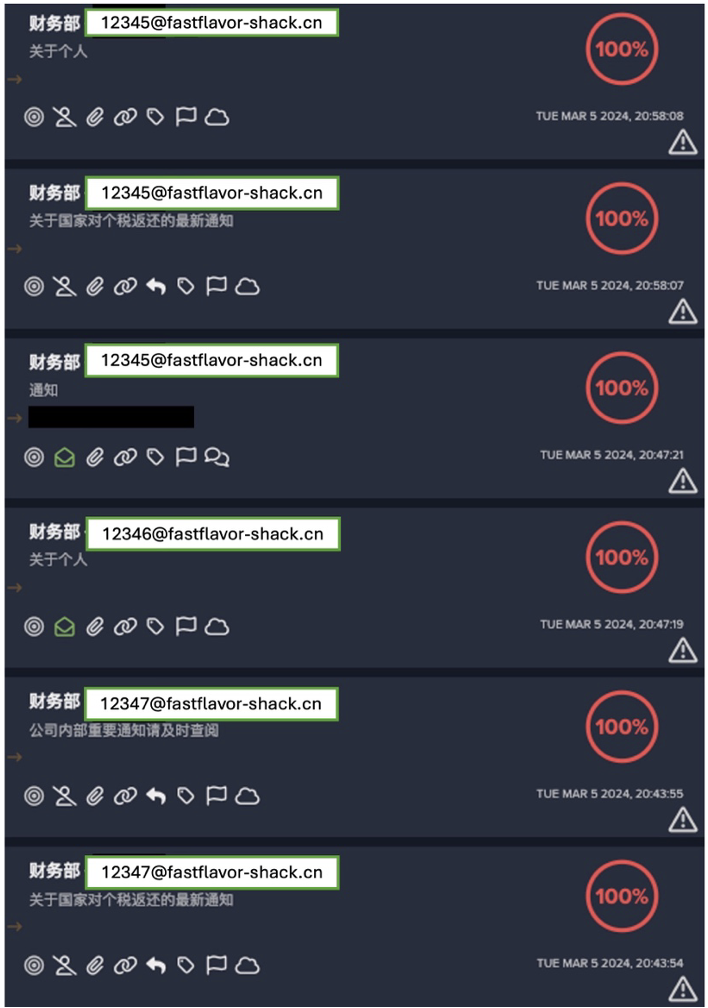
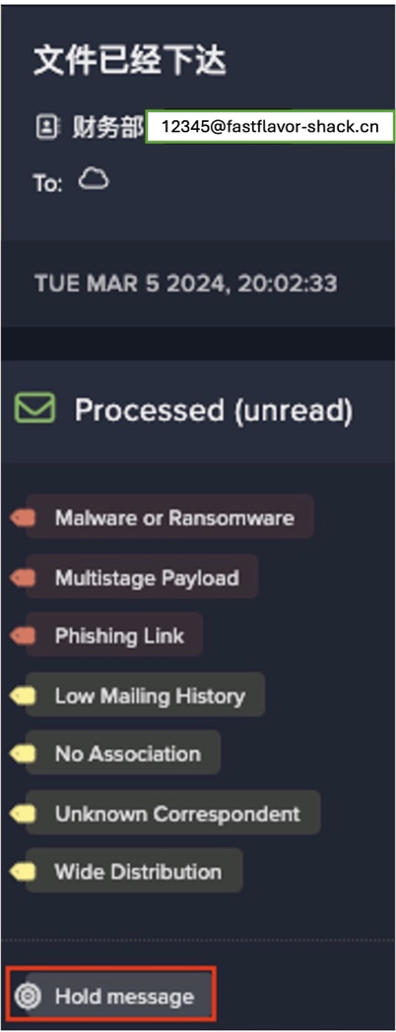
No team should be spending all of their time maintaining email security policies, releasing emails that shouldn’t have been held, or holding back emails that should have been – all the things that traditional email security solutions have almost forced them to become accustomed to. A day in the life of an admin shouldn’t include tens – and certainly not hundreds – of minutes spent in their email security dashboard.
At the moment, teams are logging in far too often, and when they do, they’re forced to make individual decisions about safe listing and blocking domains, or releasing emails. These can lead to the creation of blanket rules that open up future windows for attackers – unintended consequences that ultimately create more work in the future. This type of hand-to-hand combat puts security teams on the frontline, when their time could be much better spent doing the high-level strategic work humans are best at.
Understanding You: A Different Approach to Email Security
In today’s discussions about email security, there is a consensus that relying on a gateway is no longer feasible. The new era is one of ICES (Integrated cloud email security) solutions and other tools leveraging artificial intelligence and APIs. But there's no point adopting new technology with an old philosophy – and most of these solutions use AI to automate the same old approach: looking at past attacks to try and stop the next.
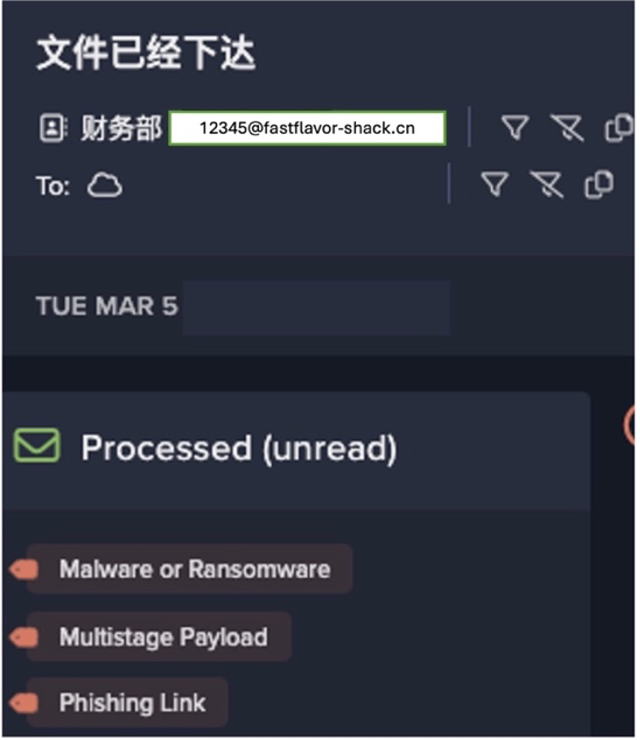
This is where Darktrace/Email takes a fundamentally different and unique approach. It’s not just about using AI; it’s about using it in the right capacity. Our AI understands you – learning where users log in from, who they email, their behavior throughout the day – to tailor the detection and response process according to their individual profile. There’s no point withholding an email if only a tiny element of it poses a risk – Darktrace/Email takes the least aggressive action required to neutralize a threat. Instead of a blanket allow-deny criteria, it can rewrite links or withhold attachments based on its knowledge of the user’s normal inbox activity. Stopping malicious emails while allowing legitimate emails through – with risky elements neutralized – lifts security teams out of the fire-fighting activities described earlier and frees up their time for more strategic and valuable decision-making.
This is going to get me to reduce my current email security stack… this is going to take it to that level that I need it to”
- Early Look Customer, Darktrace/Email
Account Takeover
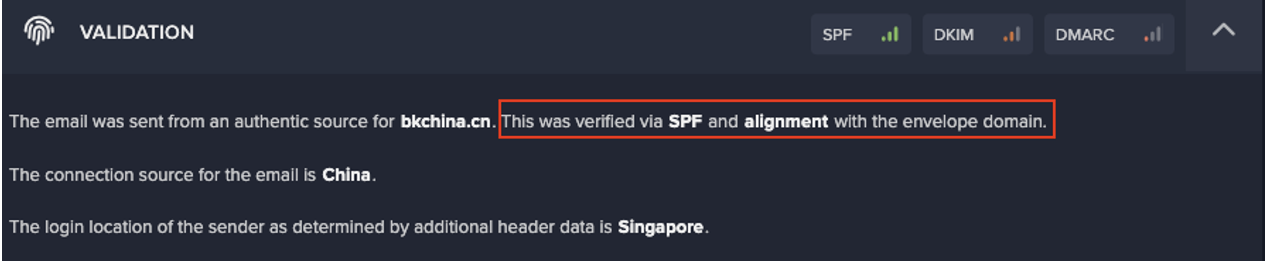
Embedded account takeover protection is an essential component of modern email security. Security teams need visibility not just over email breaches but of what happens once an attacker has control of an inbox, particularly in the most damaging use cases like Business Email Compromise (BEC) and ransomware. This entails understanding a user’s behavior in their inbox, outbound emails and beyond into their wider account activity. Darktrace captures a user’s activity across email and their Microsoft or Google account in a single pane of glass – detecting and countering all of the markers that could signify a compromised account.
Insights from other cloud applications and network devices gleaned from Darktrace's wider visibility of the business can bring a 360° understanding of the user, further enhancing detection of account takeover and other harmful activity.

What ‘user-friendly’ actually looks like
The best user interface is one that you never have to log into. In an ideal world, teams are able to visit their tools less frequently because intelligent AI is automating work previously done by humans. This is made possible by Darktrace’s precision detection and response technology, which takes appropriate action on emails and accounts to neutralize threats without disrupting day-to-day business operations.
The second-best user interface is one where you can quickly log in and get key insights fast, whether that’s regarding an action taken or the current activity of a user – and then get out. Darktrace/Email enables teams to get key information quickly, at both a high and granular level. The dashboard offers immediate insights into users and emails, with a real-time snapshot of active user identities, targeted user and actioned emails, segmented by type of attack.
At every touchpoint, Darktrace reduces friction with optimized workflows. From being able to quickly identify VIPs to safely previewing links and attachments, security teams can get the information they need without needing to switch between windows or navigate inaccessible interfaces. Explainable AI gives users natural-language summaries of individual emails or the overall health of an email environment, and simplified action flows allow security teams to personalize security for different employees – for example, sending VIPs a unique notification, or taking extra precautions around employees who work in accounting. Taken together, this meaning that admins can spend even less time managing policies.

The ideal interface is also the one that’s the most accessible to you. The mobile app guarantees convenience for security teams, making available all the main functions of the interface for on-the-go analysis at any time or place. Teams can travel or leave the office while retaining the peace of mind that if a critical incident was to occur, they would be able to get instant visibility on the data and take action without needing to get back to their desks.

With every passing day, the security team can rest easier. Every activity is taken into account to help the AI tune and adapt over time to become even better at detecting and responding to threats.
Having email on the app is going to be game changing”
- Early Look Customer, Darktrace/Email
Getting the full picture
Most often, email is the entry point from which a threat actor moves stealthily throughout an organization collecting information and assets. Most solutions look at email in isolation, without prioritizing or connecting disparate events into a wider pattern.
In contrast, Darktrace/Email integrates seamlessly with Darktrace's Cyber AI Analyst, a technology that conducts autonomous enterprise-wide investigations around every alert produced by the wider Darktrace platform. Through this integration, malicious email activity is analyzed and displayed in the context of the full security incident to which it belongs. As a result, security teams can see why and how a wider problem might have originated in email and spread to other apps, endpoints, or the wider corporate network.
Empowering employees to take an active role in security
The role of the security team can be made more difficult if employees take a lax or disengaged approach to security – or if a user is given too much control, and has the ability to make potentially dangerous decisions. Training employees on security procedures is another to-do which can easily fall to the bottom of the agenda during busy periods, especially as point-in-time phishing simulations have proven to be not particularly effective.
To this end, Darktrace/Email uses Explainable AI to say in natural language what it thought about an email, and delivers its findings not just to the security team, but optionally to the wider workforce as well. Delivered in the form of contextual banners in emails, periodic digests, or directly in Outlook, these insights transform security education from a quarterly or yearly exercise into real-time security awareness. Our next blog will dive deeper into how employee engagement can support the security team’s efforts and harden defenses throughout the organization.
Because Darktrace is built on a fundamentally different approach, it not only stops novel and targeted sophisticated attacks but allows legitimate emails to flow through. This is what makes it a truly set-and-forget technology, with the AI taking on much of the heavy lifting previously undertaken by security teams.