In an increasingly interconnected digital landscape, the prevalence of critical vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems stands as an open invitation to malicious actors. These vulnerabilities serve as a near limitless resource, granting attackers a continually array of entry points into targeted networks.
In the final week of August 2023, Darktrace observed malicious actors validating exploits for one such critical vulnerability, likely the critical RCE vulnerability, CVE-2023-38035, on Ivanti Sentry servers within multiple customer networks. Shortly after these successful tests were carried out, malicious actors were seen delivering crypto-mining and reconnaissance tools onto vulnerable Ivanti Sentry servers.
Fortunately, Darktrace DETECT™ was able to identify this post-exploitation activity on the compromised servers at the earliest possible stage, allowing the customer security teams to take action against affected devices. In environments where Darktrace RESPOND™ was enabled in autonomous response mode, Darktrace was further able inhibit the identified post-exploitation activity and stop malicious actors from progressing towards their end goals.
Exploitation of Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Products
The software provider, Ivanti, offers a variety of widely used endpoint management, service management, and security solutions. In July and August 2023, the Norwegian cybersecurity company, Mnemonic, disclosed three vulnerabilities in Ivanti products [1]/[2]/[3]; two in Ivanti's endpoint management solution, Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) (formerly called 'MobileIron Core'), and one in Ivanti’s security gateway solution, Ivanti Sentry (formerly called 'MobileIron Sentry'):
CVE-2023-35078
- CVSS Score: 10.0
- Affected Product: Ivanti EPMM
- Details from Ivanti: [4]/[5]/[6]
- Vulnerability type: Authentication bypass
CVE-2023-35081
- CVSS Score: 7.2
- Affected Product: Ivanti EPMM
- Details from Ivanti: [7]/[8]/[9]
- Vulnerability type: Directory traversal
CVE-2023-38035
- CVSS Score:
- Affected Product: Ivanti Sentry
- Details from Ivanti: [10]/[11]/[12]
- Vulnerability type: Authentication bypass
At the beginning of August 2023, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Norwegian National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC-NO) provided details of advanced persistent threat (APT) activity targeting EPMM systems within Norwegian private sector and government networks via exploitation of CVE-2023-35078 combined with suspected exploitation of CVE-2023-35081.
In an article published in August 2023 [12], Ivanti disclosed that a very limited number of their customers had been subjected to exploitation of the Ivanti Sentry vulnerability, CVE-2023-38035, and on the August 22, 2023, CISA added the Ivanti Sentry vulnerability, CVE-2023-38035 to its ‘Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalogue’. CVE-2023-38035 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability affecting the System Manager Portal of Ivanti Sentry systems. The System Manager Portal, which is accessible by default on port 8433, is used for administration of the Ivanti Sentry system. Through exploitation of CVE-2023-38035, an unauthenticated actor with access to the System Manager Portal can achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) on the underlying Ivanti Sentry system.
Observed Exploitation of CVE-2023-38035
On August 24, Darktrace observed Ivanti Sentry servers within several customer networks receiving successful SSL connections over port 8433 from the external endpoint, 34.77.65[.]112. The usage of port 8433 indicates that the System Manager Portal was accessed over the connections. Immediately after receiving these successful connections, Ivanti Sentry servers made GET requests over port 4444 to 34.77.65[.]112. The unusual string ‘Wget/1.14 (linux-gnu)’ appeared in the User-Agent headers of these requests, indicating that the command-line utility, wget, was abused to initiate the requests.

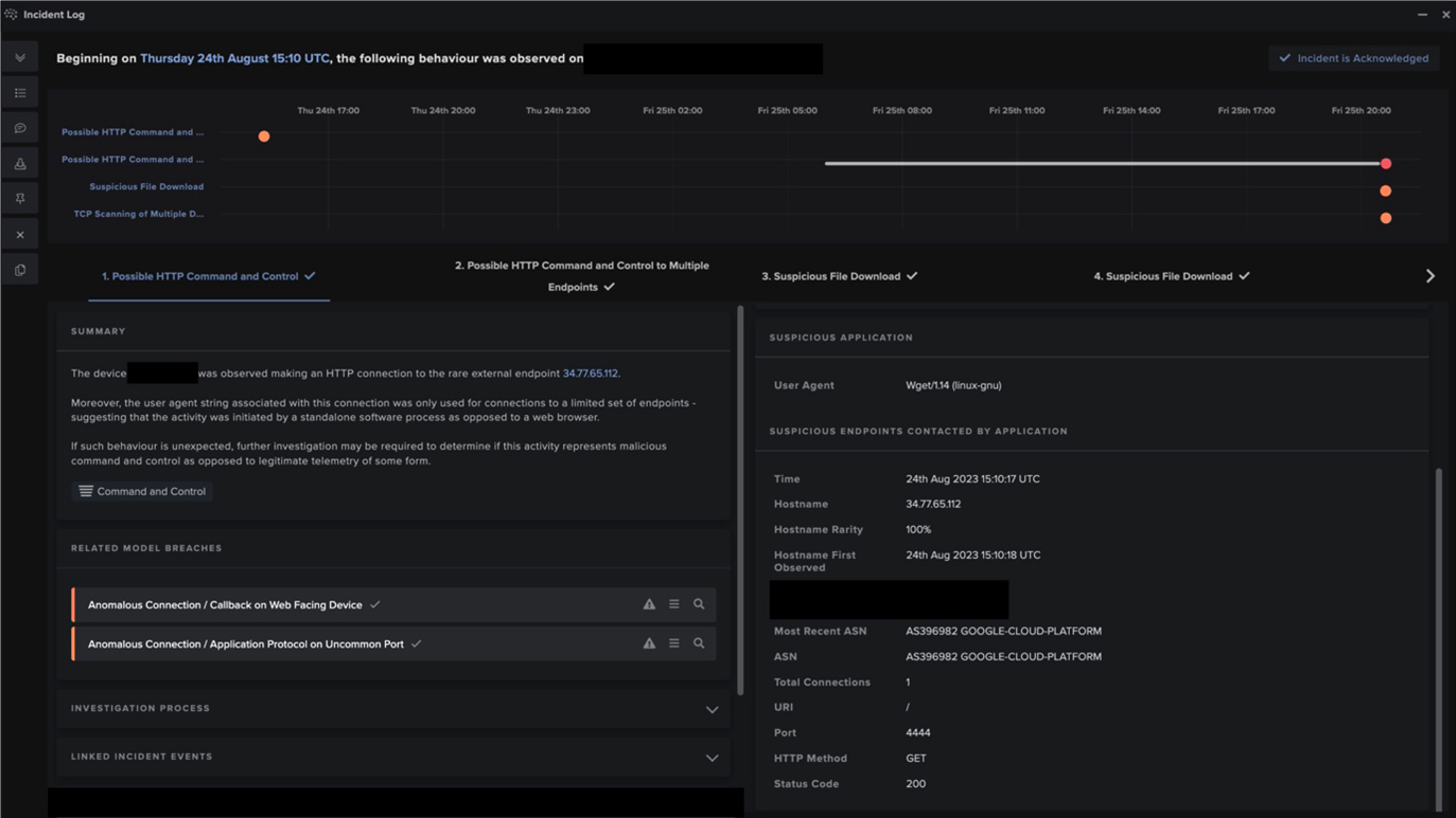
In cases where Darktrace RESPOND was enabled in autonomous response mode, RESPOND was able to automatically enforce the Ivanti Sentry server’s normal pattern of life, thus blocking further exploit testing.

The GET requests to 34.77.65[.]112 were responded to with the following HTML document:

None of the links within this HTML document were functional. Furthermore, the devices’ downloads of these HTML documents do not appear to have elicited further malicious activities. These facts suggest that the observed 34.77.65[.]112 activities were representative of a malicious actor validating exploits (likely for CVE-2023-38035) on Ivanti Sentry systems.
Over the next 24 hours, these Ivanti Sentry systems received successful SSL connections over port 8433 from a variety of suspicious external endpoints, such as 122.161.66[.]161. These connections resulted in Ivanti Sentry systems making HTTP GET requests to subdomains of ‘oast[.]site’ and ‘oast[.]live’. Strings containing ‘curl’ appeared in the User-Agent headers of these requests, indicating that the command-line utility, cURL, was abused to initiate the requests.
These ‘oast[.]site’ and ‘oast[.]live’ domains are used by the out-of-band application security testing (OAST) service, Interactsh. Malicious actors are known to abuse this service to carry out out-of-band (OOB) exploit testing. It, therefore, seems likely that these activities were also representative of a malicious actor validating exploits for CVE-2023-38035 on Ivanti Sentry systems.
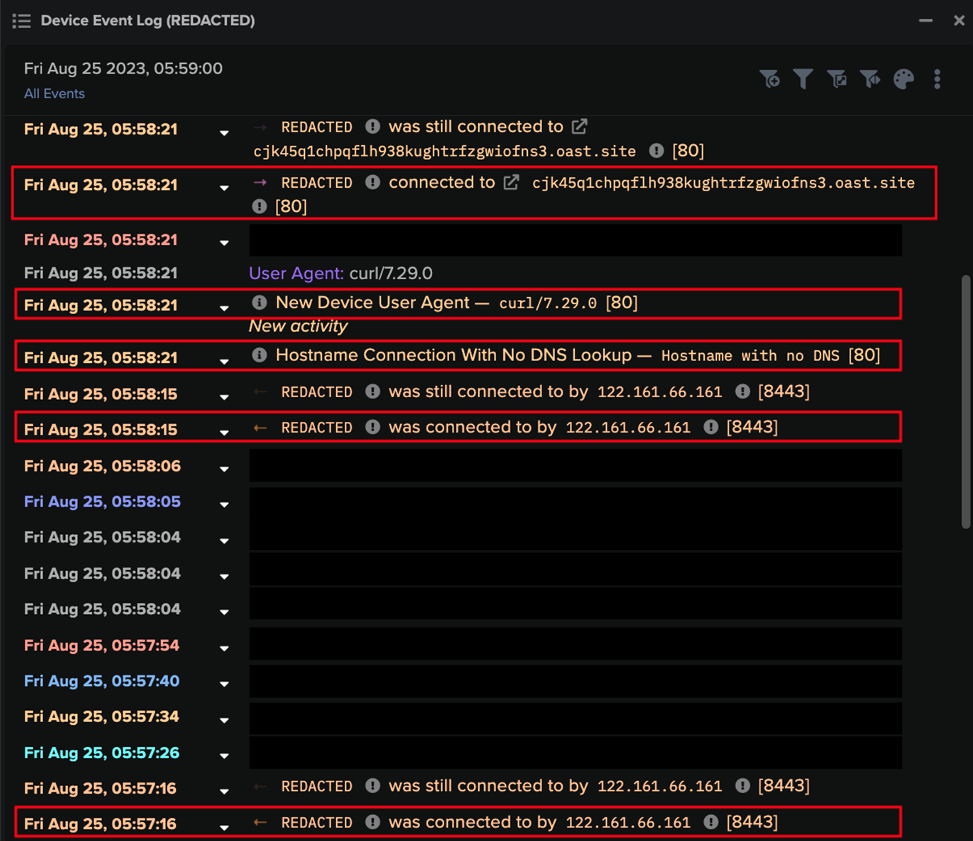
The actors seen validating exploits for CVE-2023-38035 may have been conducting such activities in preparation for their own subsequent malicious activities. However, given the variety of attack chains which ensued from these exploit validation activities, it is also possible that they were carried out by Initial Access Brokers (IABs) The activities which ensued from exploit validation activities identified by Darktrace fell into two categories: internal network reconnaissance and cryptocurrency mining.
Reconnaissance Activities
In one of the reconnaissance cases, immediately after receiving successful SSL connections over port 8443 from the external endpoints 190.2.131[.]204 and 45.159.248[.]179, an Ivanti Sentry system was seen making a long SSL connection over port 443 to 23.92.29[.]148, and making wget GET requests over port 4444 with the Target URIs '/ncat' and ‘/TxPortMap’ to the external endpoints, 45.86.162[.]147 and 195.123.240[.]183.

The Ivanti Sentry system then went on to scan for open SMB ports on systems within the internal network. This activity likely resulted from an attacker dropping a port scanning utility on the vulnerable Ivanti Sentry system.

In another reconnaissance case, Darktrace observed multiple wget HTTP requests with Target URIs such as ‘/awp.tar.gz’ and ‘/resp.tar.gz’ to a suspicious, external server (78.128.113[.]130). Shortly after making these requests, the Ivanti Sentry system started to scan for open SMB ports and to respond to LLMNR queries from other internal devices. These behaviors indicate that the server may have installed an LLMNR poisoning tool, such as Responder. The Ivanti Sentry server also went on to conduct further information-gathering activities, such as LDAP reconnaissance, HTTP-based vulnerability scanning, HTTP-based password searching, and RDP port scanning.

In cases where Darktrace RESPOND was active, reconnaissance activities resulted in RESPOND enforcing the Ivanti Sentry server’s pattern of life.


Crypto-Mining Activities
In one of the cryptomining cases, Darktrace detected an Ivanti Sentry server making SSL connections to aelix[.]xyz and mining pool endpoints after receiving successful SSL connections over port 8443 from the external endpoint, 140.228.24[.]160.

In a cryptomining case on another customer’s network, an Ivanti Sentry server was seen making GET requests indicative of Kinsing malware infection. These requests included wget GET requests to 185.122.204[.]197 with the Target URIs ‘/unk.sh’ and ‘/se.sh’ and a combination of GET and POST requests to 185.221.154[.]208 with the User-Agent header ‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/99.0.4844.51 Safari/537.36’ and the Target URIs, ‘/mg’, ‘/ki’, ‘/get’, ‘/h2’, ‘/ms’, and ‘/mu’. These network-based artefacts have been observed in previous Kinsing infections [13].

On customer environments where RESPOND was active, Darktrace was able to take swift autonomous action by blocking cryptomining connection attempts to malicious command-and-control (C2) infrastructure, in this case Kinsing servers.

Fortunately, due to Darktrace DETECT+RESPOND prompt identification and targeted actions against these emerging threats, coupled with remediating steps taken by affected customers’ security teams, neither the cryptocurrency mining activities nor the network reconnaissance activities led to significant disruption.

Conclusion The inevitable presence of critical vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems underscores the perpetual challenge of defending against malicious intrusions. The near inexhaustible supply of entry routes into organizations’ networks available to malicious actors necessitates a more proactive and vigilant approach to network security.
While it is, of course, essential for organizations to secure their digital environments through the regular patching of software and keeping abreast of developing vulnerabilities that could impact their network, it is equally important to have a safeguard in place to mitigate against attackers who do manage to exploit newly discovered vulnerabilities.
In the case of Ivanti Sentry, Darktrace observed malicious actors validating exploits against affected servers on customer networks just a few days after the public disclosure of the critical vulnerability. This activity was followed up by a variety of malicious and disruptive, activities including cryptocurrency mining and internal network reconnaissance.
Darktrace DETECT immediately detected post-exploitation activities on compromised Ivanti Sentry servers, enabling security teams to intervene at the earliest possible stage. Darktrace RESPOND, when active, autonomously inhibited detected post-exploitation activities. These DETECT detections, along with their accompanying RESPOND interventions, prevented malicious actors from being able to progress further towards their likely harmful objectives.
Credit to Sam Lister, Senior Cyber Analyst, and Trent Kessler, SOC Analyst
Appendices
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Initial Access techniques:
- Exploit Public-Facing Application (T1190)
Credential Access techniques:
- Unsecured Credentials: Credentials In Files (T1552.001)
- Adversary-in-the-Middle: LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning and SMB Relay (T1557.001)
Discovery
- Network Service Discovery (T1046)
- Remote System Discovery (T1018)
- Account Discovery: Domain Account (T1087.002)
Command and Control techniques:
- Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols (T1071.001)
- Ingress Tool Transfer (T1105)
- Non-Standard Port (T1571)
- Encrypted Channel: Asymmetric Cryptography (T1573.002)
Impact techniques
- Resource Hijacking (T1496)
List of IoCs
Exploit testing IoCs:
· 34.77.65[.]112
· Wget/1.14 (linux-gnu)
· cjjovo7mhpt7geo8aqlgxp7ypod6dqaiz.oast[.]site • 178.128.16[.]97
· curl/7.19.7 (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.27.1 zlib/1.2.3 libidn/1.18 libssh2/1.4.2
· cjk45q1chpqflh938kughtrfzgwiofns3.oast[.]site • 178.128.16[.]97
· curl/7.29.0
Kinsing-related IoCs:
· 185.122.204[.]197
· /unk.sh
· /se.sh
· 185.221.154[.]208
· 185.221.154[.]208
· 45.15.158[.]124
· Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/99.0.4844.51 Safari/537.36
· /mg
· /ki
· /get
· /h2
· /ms
· /mu
· vocaltube[.]ru • 185.154.53[.]140
· 92.255.110[.]4
· 194.87.254[.]160
Responder-related IoCs:
· 78.128.113[.]130
· 78.128.113[.]34
· /awp.tar.gz
· /ivanty
· /resp.tar.gz
Crypto-miner related IoCs:
· 140.228.24[.]160
· aelix[.]xyz • 104.21.60[.]147 / 172.67.197[.]200
· c8446f59cca2149cb5f56ced4b448c8d (JA3 client fingerprint)
· b5eefe582e146aed29a21747a572e11c (JA3 client fingerprint)
· pool.supportxmr[.]com
· xmr.2miners[.]com
· xmr.2miners[.]com
· monerooceans[.]stream
· xmr-eu2.nanopool[.]org
Port scanner-related IoCs:
· 122.161.66[.]161
· 192.241.235[.]32
· 45.86.162[.]147
· /ncat
· Wget/1.14 (linux-gnu)
· 45.159.248[.]179
· 142.93.115[.]146
· 23.92.29[.]148
· /TxPortMap
· 195.123.240.183
· 6935a8d379e086ea1aed159b8abcb0bc8acf220bd1cbc0a84fd806f14014bca7 (SHA256 hash of downloaded file)
Darktrace DETECT Model Breaches
· Anomalous Server Activity / New User Agent from Internet Facing System
· Device / New User Agent
· Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
· Device / New User Agent and New IP
· Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port
· Anomalous Connection / Callback on Web Facing Device
· Compromise / High Volume of Connections with Beacon Score
· Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections
· Compromise / High Volume of Connections with Beacon Score
· Compromise / Beacon for 4 Days
· Compromise / Agent Beacon (Short Period)
· Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
· Anomalous Server Activity / Rare External from Server
· Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Successful Connections
· Compromise / Monero Mining
· Compromise / High Priority Crypto Currency Mining
· Compromise / Sustained TCP Beaconing Activity To Rare Endpoint
· Device / Internet Facing Device with High Priority Alert
· Device / Suspicious SMB Scanning Activity
· Device / Internet Facing Device with High Priority Alert
· Device / Network Scan
· Device / Unusual LDAP Bind and Search Activity
· Compliance / Vulnerable Name Resolution
· Device / Anomalous SMB Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
· Device / New User Agent To Internal Server
· Anomalous Connection / Suspicious HTTP Activity
· Anomalous Connection / Unusual Internal Connections
· Anomalous Connection / Suspicious HTTP Activity
· Device / RDP Scan
· Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
· Compromise / Beaconing Activity To External Rare
· Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint
· Anomalous Connection / Suspicious HTTP Activity
· Compromise / Suspicious Internal Use Of Web Protocol
· Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External Location
· Anomalous File / Internet Facing System File Download
· Device / Suspicious SMB Scanning Activity
· Device / Internet Facing Device with High Priority Alert
· Device / Network Scan
· Device / Initial Breach Chain Compromise
References
[1] https://www.mnemonic.io/resources/blog/ivanti-endpoint-manager-mobile-epmm-authentication-bypass-vulnerability/
[2] https://www.mnemonic.io/resources/blog/threat-advisory-remote-file-write-vulnerability-in-ivanti-epmm/
[3] https://www.mnemonic.io/resources/blog/threat-advisory-remote-code-execution-vulnerability-in-ivanti-sentry/
[4] https://www.ivanti.com/blog/cve-2023-35078-new-ivanti-epmm-vulnerability
[5] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/CVE-2023-35078-Remote-unauthenticated-API-access-vulnerability?language=en_US
[6] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/KB-Remote-unauthenticated-API-access-vulnerability-CVE-2023-35078?language=en_US
[7] https://www.ivanti.com/blog/cve-2023-35081-new-ivanti-epmm-vulnerability
[8] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/CVE-2023-35081-Arbitrary-File-Write?language=en_US
[9] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/KB-Arbitrary-File-Write-CVE-2023-35081?language=en_US
[10] https://www.ivanti.com/blog/cve-2023-38035-vulnerability-affecting-ivanti-sentry
[11] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/CVE-2023-38035-API-Authentication-Bypass-on-Sentry-Administrator-Interface?language=en_US
[12] https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/KB-API-Authentication-Bypass-on-Sentry-Administrator-Interface-CVE-2023-38035?language=en_US
[13] https://isc.sans.edu/diary/Your+Business+Data+and+Machine+Learning+at+Risk+Attacks+Against+Apache+NiFi/29900